what forms during the zygote period to cushion and protect the zygote
half dozen.1 Conception and Prenatal Development
Learning Objectives
- Review the stages of prenatal development.
- Explicate how the developing embryo and fetus may be harmed by the presence of teratogens and describe what a female parent can do to reduce her hazard.
Conception occurs when an egg from the mother is fertilized by a sperm from the father. In humans, the conception procedure begins with ovulation, when an ovum, or egg (the largest prison cell in the human being trunk), which has been stored in 1 of the mother's two ovaries, matures and is released into the fallopian tube. Ovulation occurs about halfway through the woman'due south menstrual cycle and is aided past the release of a complex combination of hormones. In addition to helping the egg mature, the hormones also cause the lining of the uterus to grow thicker and more than suitable for implantation of a fertilized egg.
If the woman has had sexual intercourse within 1 or ii days of the egg'southward maturation, one of the upwardly to 500 one thousand thousand sperm deposited by the man's ejaculation, which are traveling up the fallopian tube, may fertilize the egg. Although few of the sperm are able to brand the long journey, some of the strongest swimmers succeed in meeting the egg. As the sperm attain the egg in the fallopian tube, they release enzymes that assail the outer jellylike protective coating of the egg, each trying to be the commencement to enter. As soon as one of the millions of sperm enters the egg'southward coating, the egg immediately responds by both blocking out all other challengers and at the same time pulling in the single successful sperm.
The Zygote
Within several hours, half of the 23 chromosomes from the egg and half of the 23 chromosomes from the sperm fuse together, creating a zygote—a fertilized ovum. The zygote continues to travel down the fallopian tube to the uterus. Although the uterus is only nigh 4 inches away in the woman'due south body, this is yet a substantial journeying for a microscopic organism, and fewer than one-half of zygotes survive across this earliest phase of life. If the zygote is still viable when it completes the journey, it volition attach itself to the wall of the uterus, but if it is not, it will exist flushed out in the adult female's menstrual flow. During this fourth dimension, the cells in the zygote continue to divide: The original 2 cells become four, those four become eight, and and so on, until there are thousands (and eventually trillions) of cells. Soon the cells begin to differentiate, each taking on a separate function. The earliest differentiation is between the cells on the inside of the zygote, which volition begin to form the developing man, and the cells on the outside, which volition form the protective environs that will provide support for the new life throughout the pregnancy.
The Embryo
In one case the zygote attaches to the wall of the uterus, information technology is known as the embryo. During the embryonic phase, which will concluding for the side by side 6 weeks, the major internal and external organs are formed, each beginning at the microscopic level, with only a few cells. The changes in the embryo's advent will continue rapidly from this point until birth.
While the inner layer of embryonic cells is busy forming the embryo itself, the outer layer is forming the surrounding protective surround that will assistance the embryo survive the pregnancy. This environs consists of 3 major structures: The amniotic sac is the fluid-filled reservoir in which the embryo (shortly to be known every bit a fetus) volition live until birth, and which acts every bit both a cushion confronting outside pressure and as a temperature regulator. The placenta is an organ that allows the exchange of nutrients between the embryo and the mother, while at the aforementioned time filtering out harmful material. The filtering occurs through a thin membrane that separates the mother's claret from the blood of the fetus, allowing them to share only the cloth that is able to pass through the filter. Finally, the umbilical cord links the embryo directly to the placenta and transfers all cloth to the fetus. Thus the placenta and the umbilical cord protect the fetus from many strange agents in the mother'south system that might otherwise pose a threat.
The Fetus
Beginning in the 9th week after conception, the embryo becomes a fetus. The defining characteristic of the fetal stage is growth. All the major aspects of the growing organism have been formed in the embryonic stage, and now the fetus has approximately six months to go from weighing less than an ounce to weighing an average of half-dozen to 8 pounds. That'southward quite a growth spurt.
The fetus begins to take on many of the characteristics of a homo being, including moving (by the 3rd month the fetus is able to coil and open its fingers, course fists, and wiggle its toes), sleeping, likewise every bit early forms of swallowing and animate. The fetus begins to develop its senses, condign able to distinguish tastes and respond to sounds. Research has found that the fetus even develops some initial preferences. A newborn prefers the mother'southward voice to that of a stranger, the languages heard in the womb over other languages (DeCasper & Fifer, 1980; Moon, Cooper, & Fifer, 1993), and even the kinds of foods that the mother ate during the pregnancy (Mennella, Jagnow, & Beauchamp, 2001). Past the end of the tertiary month of pregnancy, the sexual organs are visible.
How the Surround Can Bear upon the Vulnerable Fetus
Prenatal development is a complicated process and may not always go every bit planned. Virtually 45% of pregnancies result in a miscarriage, often without the female parent ever being enlightened it has occurred (Moore & Persaud, 1993). Although the amniotic sac and the placenta are designed to protect the embryo, substances that can harm the fetus, known every bit teratogens, may yet cause problems. Teratogens include full general environmental factors, such equally air pollution and radiations, but likewise the cigarettes, alcohol, and drugs that the female parent may use. Teratogens do non ever damage the fetus, simply they are more probable to exercise and then when they occur in larger amounts, for longer time periods, and during the more sensitive phases, as when the fetus is growing nearly chop-chop. The nigh vulnerable menstruation for many of the fetal organs is very early on in the pregnancy—before the mother even knows she is pregnant.
Harmful substances that the mother ingests may harm the child. Cigarette smoking, for example, reduces the blood oxygen for both the mother and child and can cause a fetus to be born severely underweight. Another serious threat is fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), a status caused past maternal alcohol drinking that can atomic number 82 to numerous detrimental developmental furnishings, including limb and facial abnormalities, genital anomalies, and mental retardation. 1 in about every 500 babies in the United States is born with fetal alcohol syndrome, and it is considered one of the leading causes of retardation in the world today (Niccols, 1994). Because there is no known safe level of booze consumption for a significant woman, the U.Due south. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicates that "a pregnant woman should not drink alcohol" (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2005). Therefore, the best approach for expectant mothers is to avoid alcohol completely. Maternal drug abuse is likewise of major concern and is considered one of the greatest risk factors facing unborn children.
Figure 6.1
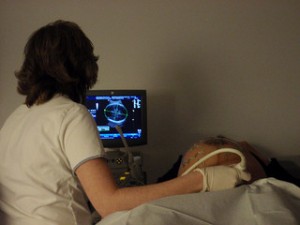 Daniel Lobo – Ecografía – CC BY 2.0.
Daniel Lobo – Ecografía – CC BY 2.0.
Prenatal screenings, including a sonogram, assistance detect potential nascence defects and other potentially unsafe conditions.
The environment in which the mother is living too has a major affect on infant development (Duncan & Brooks-Gunn, 2000; Haber & Toro, 2004). Children built-in into homelessness or poverty are more probable to have mothers who are malnourished, who suffer from domestic violence, stress, and other psychological problems, and who smoke or abuse drugs. And children built-in into poverty are also more likely to exist exposed to teratogens. Poverty'southward impact may also amplify other issues, creating substantial problems for healthy child development (Evans & English, 2002; Gunnar & Quevedo, 2007).
Mothers normally receive genetic and blood tests during the kickoff months of pregnancy to make up one's mind the health of the embryo or fetus. They may undergo sonogram, ultrasound, amniocentesis, or other testing. The screenings notice potential birth defects, including neural tube defects, chromosomal abnormalities (such equally Down syndrome), genetic diseases, and other potentially unsafe conditions. Early diagnosis of prenatal problems can allow medical handling to amend the health of the fetus.
Key Takeaways
- Evolution begins at the moment of conception, when the sperm from the father merges with the egg from the female parent.
- Within a span of 9 months, evolution progresses from a single cell into a zygote and and so into an embryo and fetus.
- The fetus is connected to the female parent through the umbilical cord and the placenta, which let the fetus and mother to exchange nourishment and waste. The fetus is protected by the amniotic sac.
- The embryo and fetus are vulnerable and may be harmed by the presence of teratogens.
- Smoking, alcohol apply, and drug utilise are all probable to exist harmful to the developing embryo or fetus, and the mother should entirely refrain from these behaviors during pregnancy or if she expects to become significant.
- Environmental factors, especially homelessness and poverty, have a substantial negative effect on salubrious child development.
Exercises and Critical Thinking
- What behaviors must a woman avert engaging in when she decides to try to become meaning, or when she finds out she is pregnant? Do you think the power of a mother to appoint in healthy behaviors should influence her choice to accept a kid?
- Given the negative effects of poverty on man development, what steps do yous think that societies should take to attempt to reduce poverty?
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2005). Alcohol use and pregnancy. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/factsheets/FAS_alcoholuse.pdf
DeCasper, A. J., & Fifer, Due west. P. (1980). Of homo bonding: Newborns adopt their mothers' voices. Science, 208, 1174–1176;
Duncan, M., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (2000). Family poverty, welfare reform, and child evolution. Child Development, 71(one), 188–196;
Evans, One thousand. Due west., & English, Yard. (2002). The environment of poverty: Multiple stressor exposure, psychophysiological stress, and socio-emotional aligning. Kid Development, 73(4), 1238–1248;
Gunnar, M., & Quevedo, 1000. (2007). The neurobiology of stress and evolution. Almanac Review of Psychology, 58, 145–173.
Haber, M., & Toro, P. (2004). Homelessness amidst families, children, and adolescents: An ecological–developmental perspective. Clinical Child and Family unit Psychology Review, 7(3), 123–164.
Mennella, J. A., Jagnow, C. P., & Beauchamp, One thousand. K. (2001). Prenatal and postnatal flavor learning by human infants. Pediatrics, 107(6), e88.
Moon, C., Cooper, R. P., & Fifer, W. P. (1993). Ii-day-olds prefer their native language. Infant Behavior & Development, 16, 495–500.
Moore, G., & Persaud, T. (1993). The developing human: Clinically oriented embryology (5th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders.
Niccols, One thousand. A. (1994). Fetal booze syndrome: Implications for psychologists. Clinical Psychology Review, 14, 91–111.
Source: https://open.lib.umn.edu/intropsyc/chapter/6-1-conception-and-prenatal-development/
0 Response to "what forms during the zygote period to cushion and protect the zygote"
Post a Comment